This chapter describes how to use the Oracle JDeveloper wizards and tools to create a basic ADF Mobile application and also describes the artifacts that are automatically generated when you create an application.
This chapter includes the following sections:
You can create, deploy, and test an ADF Mobile application without writing a line of code because the JDeveloper design experience is enhanced to include support of ADF Mobile application development.
The ADF Mobile extension provides JDeveloper with the application templates that seed the completed project with basic files. The first steps in building an ADF Mobile application are to assign it a name and to specify a directory where its source files will be saved. By creating an application with the application templates provided by JDeveloper, the workspace is automatically organized into projects, along with the required configuration files.
You create an application using the application creation wizard.
Before you begin:
You must download the ADF Mobile application extension. For more information, see Section 3.3, "Setting Up JDeveloper." You may need to download and configure the ADF Mobile application extension for all target platforms. Complex applications with native features (that is, features that integrate with an operating system's native controls) may require additional SHLIB_PATH and CLASSPATH variables.
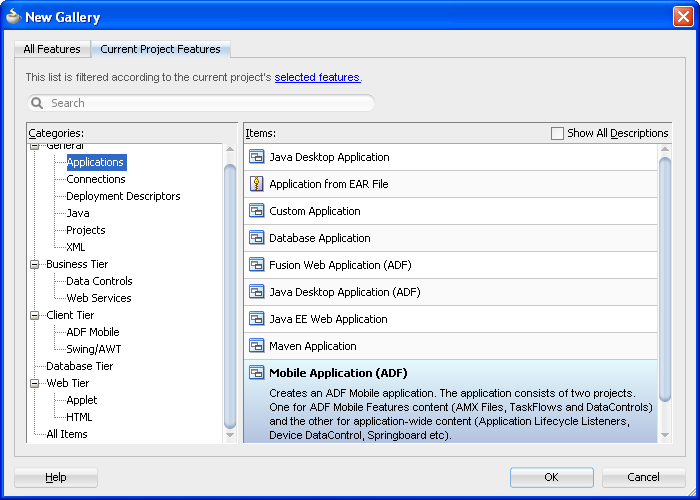
To create an ADF Mobile application:

Figure 4-1 Selecting the ADF Mobile Application Template
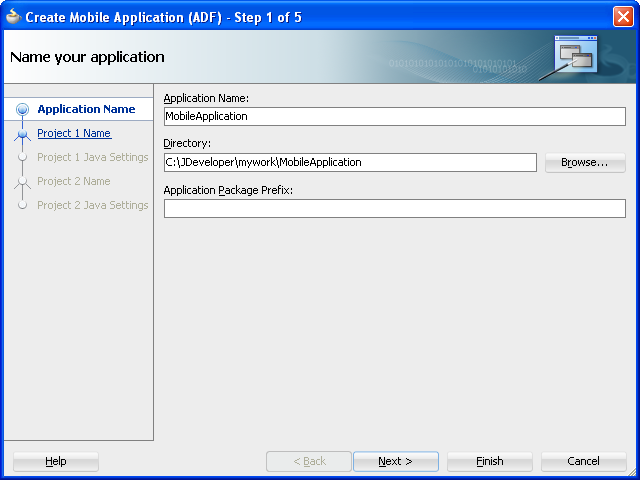
Figure 4-2 Naming the ADF Mobile Application
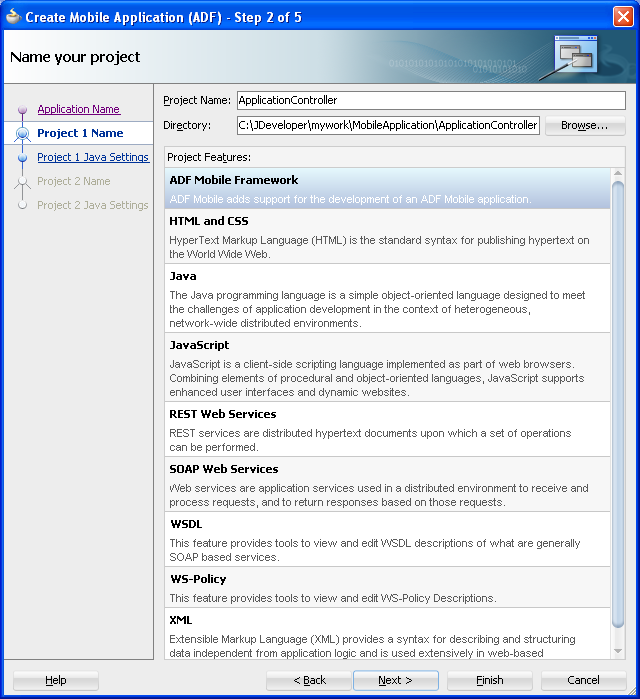
Figure 4-3 The Application Controller Project and Its Project Features
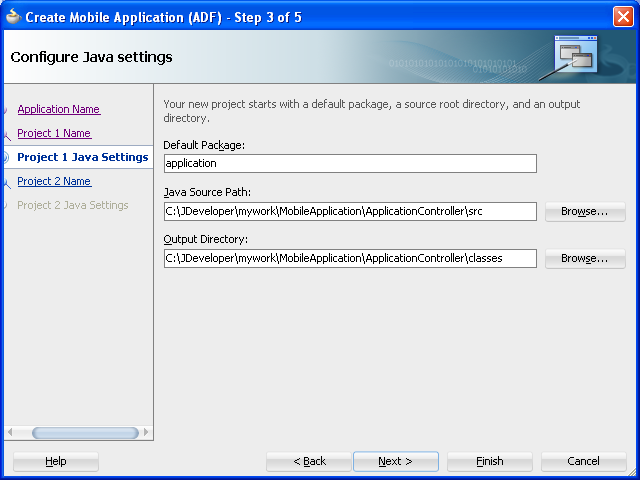
Figure 4-4 Configuring the Java Settings for the Application Controller Project
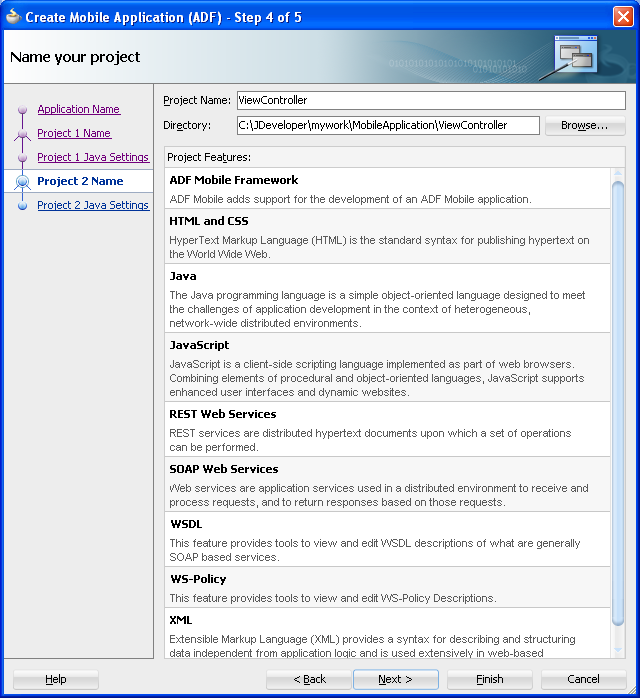
Figure 4-5 The ADF Mobile View Controller Project
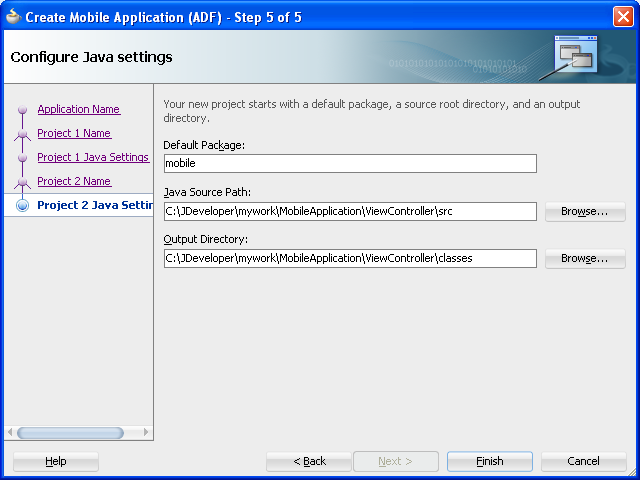
Figure 4-6 The Java Settings for the View Controller Project
In addition to creating an ADF Mobile application following the above-mentioned steps, you can open the HelloWorld sample application (located in the PublicSamples.zip file within the jdev_install /jdeveloper/jdev/extensions/oracle.adf.mobile/Samples directory on your development computer) and view the artifacts that JDeveloper generates after you complete the application creation wizard.
After you complete an ADF Mobile application project, JDeveloper adds application-level and project-level artifacts, which you access from the Application Navigator shown in Figure 4-7. In addition, JDeveloper creates the DeviceFeatures data control. The PhoneGap Java API is abstracted through this data control, thus enabling the application features implemented as ADF Mobile AMX to access various services embedded on the device. JDeveloper also creates the ApplicationFeatures data control, which enables you to build a springboard page. By dragging and dropping the operations provided by the DeviceFeatures data control into an ADF Mobile AMX page (which is described in Section 9.5, "Using the DeviceFeatures Data Control"), you add functions to manage the user contacts stored on the device, create and send both e-mail and SMS text messages, ascertain the location of the device, use the device's camera, and retrieve images stored in the device's file system.
Figure 4-7 JDeveloper-Generated ADF Mobile Application Artifacts
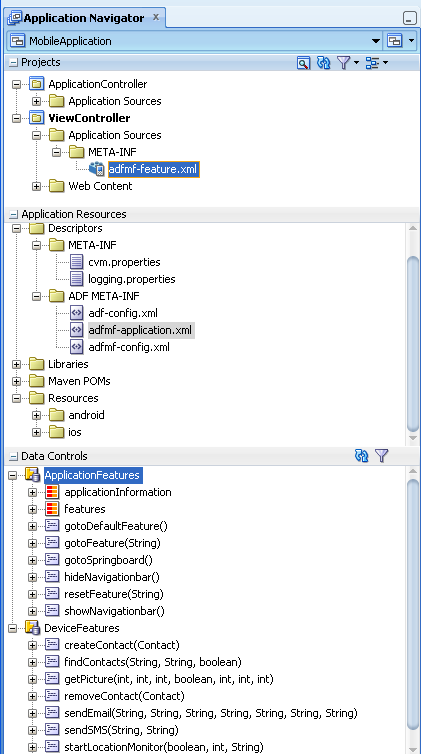
JDeveloper generates the files for ADF Mobile application in the application controller project. These files, described in Table 4-1, contain configuration files for describing the metadata of the of the ADF Mobile application. You access these files from the Application Resources pane of the Application Navigator, shown in Figure 4-8.
Figure 4-8 Mobile Application Artifacts Accessed from the Application Resources Pane
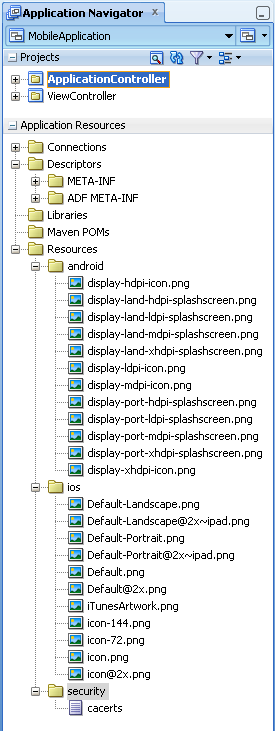
The application controller project, which houses the application-wide resources, provides the presentation layer of the ADF Mobile application in that it includes metadata files for configuring how the application will display on a mobile device. This project dictates the security for the ADF Mobile application and can include the application's login page, an application-wide resource. The application controller project is essentially a consumer of the view controller project, which defines the application features and their content. For more information, see Section 4.2.2.2, "About the View Controller Project."
Table 4-1 Mobile Application-Level Artifacts Accessed Through Application Resources
application workspace_directory \.adf\Meta-INF
A stub XML application descriptor file that enables you to define the ADF Mobile application. Similar to the application descriptors for ADF Fusion Web applications, this file enables you to define the content for an application, its navigation behavior, and its user authentication requirements. For more information, see Section 5.2, "About the Mobile Application Configuration File."
application workspace_directory \.adf\Meta-INF
Use to configure the default skin used for ADF Mobile applications. For more information, see Section 5.11, "Skinning ADF Mobile Applications."
application workspace_directory \ Application Resources\resources\ios
A set of images required for the deployment of iOS and Android applications. These include PNG images for application icons and splash screens. Deployment to an iOS-powered device, such as an iPhone, requires a set of images in varying sizes.
The default iOS images provided with the project include:
application workspace_directory \ Application Resources\resources\Security\cacerts
The cacerts certificate file, a system-wide keystore that identifies the CA certifcates to JVM 1.4. You can update this file using the Java keytool utility. You can create a custom certificate file using keytool as described in Section 17.5, "Adding Private Certificates." Any certificate file must reside within the Security directory.
application workspace_directory \src\.META-INF\logging.properties
Enables you to set the application error logging, such as the logging level and logging console. For more information, see Section 18.5, "Using and Configuring Logging."
application workspace_directory \src\.META-INF\cvm.properties
The configuration file for the Java virtual machine, JVM 1.4. Use this file to configure the application startup and heap space allotment, as well as Java and JavaScript debugging options. For more information, see Section 18.3.4, "How to Enable Debugging of Java Code and JavaScript."
application workspace_directory \Mobile Application\.adf\META-INF
Used to configure application-level settings, including the Configuration Service parameters. For more information, see the "adf-config.xml" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework . See also Section 10.7, "Administering Web Services."
application workspace_directory \ Mobile Application\.adf\META-INF
The repository for all of the connections defined in the ADF Mobile application. See also the "connections.xml" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework .
Within the application controller project itself, shown in Figure 4-9, JDeveloper creates the following artifacts, listed in Table 4-2.
Figure 4-9 The Application Controller Project
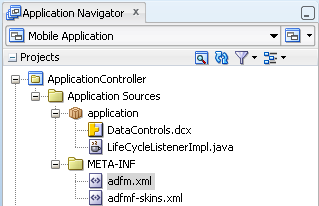
Table 4-2 Application Controller Artifacts
Defines the available skins and also enables you to define new skins.
Maintains the paths (and relative paths) for the .cpx , .dcx , .jpx , and .xcfg files (registries of metadata). For more information, see the "adfm.xml" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework .
The data controls registry. For information on using the DeviceFeature data control, which leverage the services of the device, see Section 9, "Using Bindings and Creating Data Controls." For information on the ApplicationFeatures data control, which enables you to create a springboard page that calls the embedded application features, see Section 5.4.5, "What You May Need to Know About Custom Springboard Application Features with ADF Mobile AMX Content." For more information see the "Oracle ADF Data Binding Files" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework .
The view controller project (which is generated with the default name, ViewController , as illustrated in Figure 4-10) houses the resources for the application features. Unlike the application controller project described in Section 4.2.2.1, "About the Application-Level Resources," the view controller project's metadata files describe the resources at the application feature-level, in particular the various application features that can be aggregated into an ADF Mobile application so that they can display on a mobile device within the springboard of the ADF Mobile application itself or its navigation bar at runtime. Further, the application feature metadata files describe whether the application feature is comprised of HTML or ADF Mobile AMX pages. In addition, the view controller project can include these application pages as well as application feature-level resources, such as icon images to represent the application feature on the springboard and navigation bar defined for the ADF Mobile application.
The view controller project can be decoupled from the application controller project and deployed as an archive file for reuse in other mobile applications as described in Section 5.12, "Working with Feature Archive Files." In rare cases, an application controller project can consume more than one view controller project.
Figure 4-10 The View Controller Project
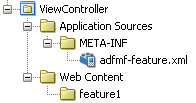
As shown in Table 4-3, these resources include the configuration file for application features called adfmf-feature.xml .
Table 4-3 View Controller Artifacts
A stub XML descriptor file that enables you to define application features. For more information, see Section 5.7, "About the Mobile Feature Application Configuration File." After you have configured the Mobile Preferences as described in Section 3.3.1, "How to Configure the Development Environment for Platforms and Form Factors," you can deploy this application using the default deployment profile settings. For more information, see Chapter 16, "Deploying ADF Mobile Applications."
The application features defined in adfmf-feature.xml display in the public_html directory. Mobile contents can include ADF Mobile AMX pages, CSS files, and task flows. Any custom images that you add to an application feature must be located within this directory. For more information, see Section 5.9.2, "What You May Need to Know About Selecting External Resources."
Creating an application results in the generation of the adfmf-application.xml file, which enables you to configure the mobile application and also the adfmf-features.xml file, which you use to add, remove, or edit the application features embedded within the mobile application. The ADF Mobile extension provides you with overview editors for both of these files, enabling you to declaratively change them. Figure 4-11 shows an example of the overview editor of the adfmf-application.xml file.
Figure 4-11 The Overview Editor of the Mobile Application
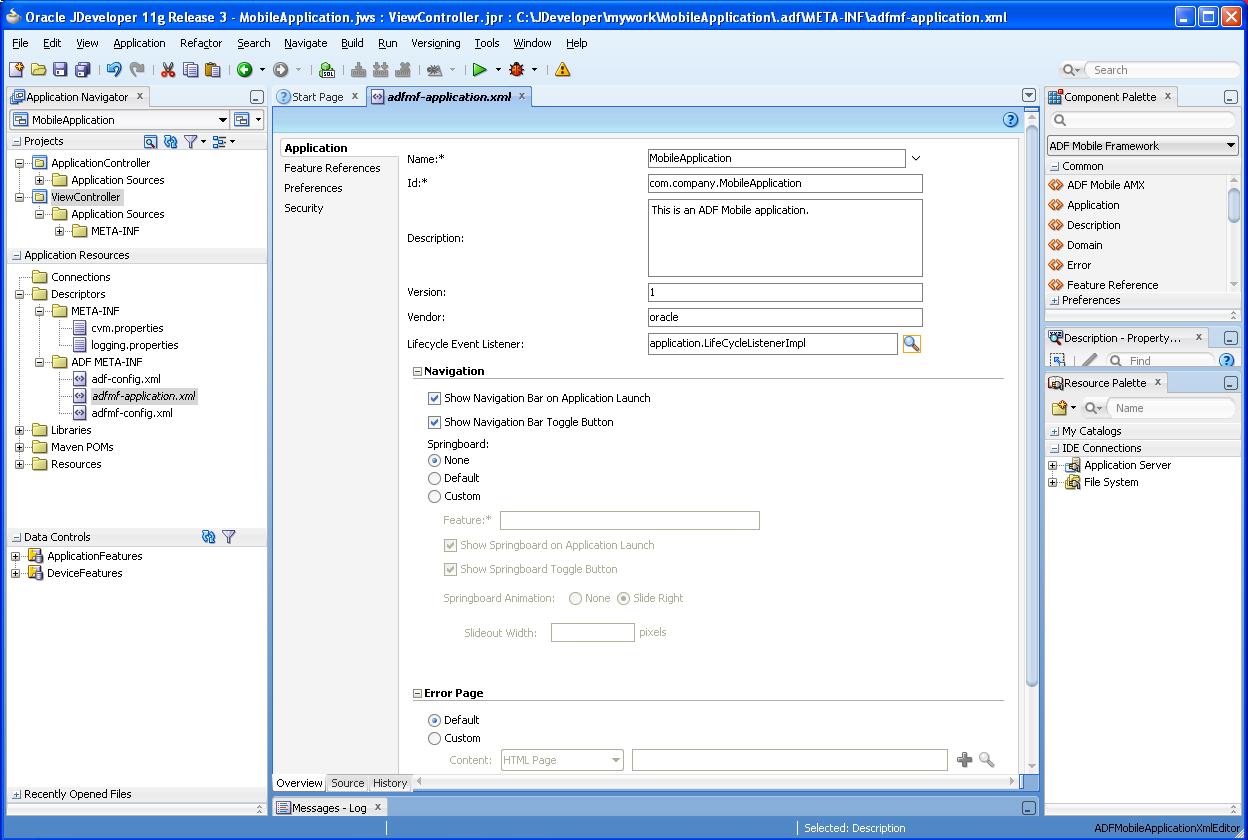
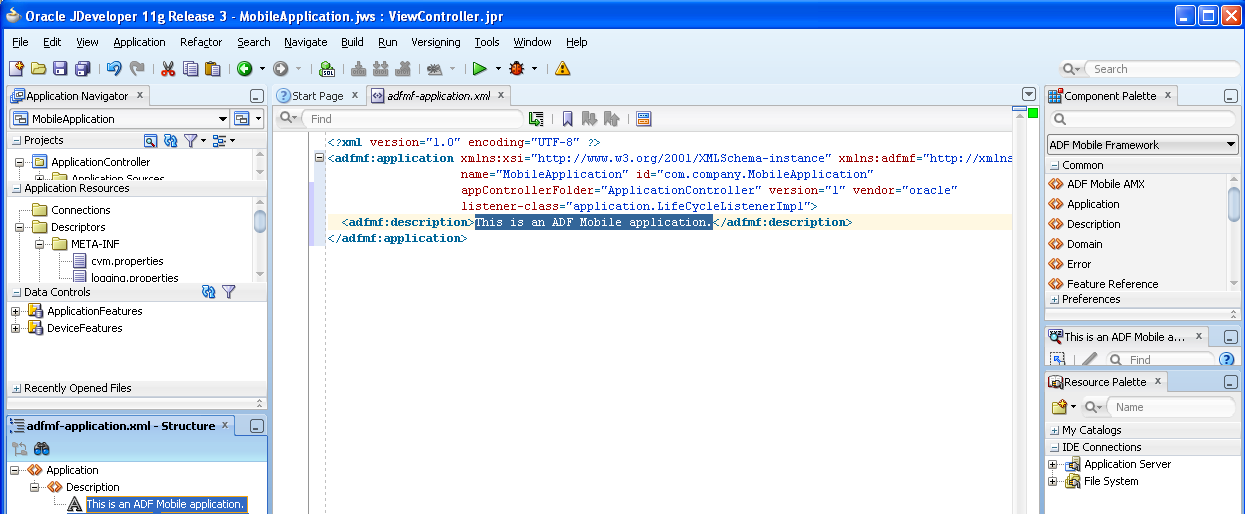
As shown in Figure 4-11, the adfmf-application.xml file is located in the Application Navigator in the Application Resources panel, under the Descriptors and ADF META-INF nodes. You can open this file by double-clicking it from this location. When you access this file, JDeveloper not only opens the associated overview editor, but also displays the pertinent page components in the component palette, which you can drag and drop into either the Source page of the editor or the Structure window, as shown in Figure 4-12. Section 5.2, "About the Mobile Application Configuration File" describes the components of the adfmf-application.xml page.
Figure 4-12 Using the Source Editor, Structure Window, and Properties Editor for the ADF Mobile Application
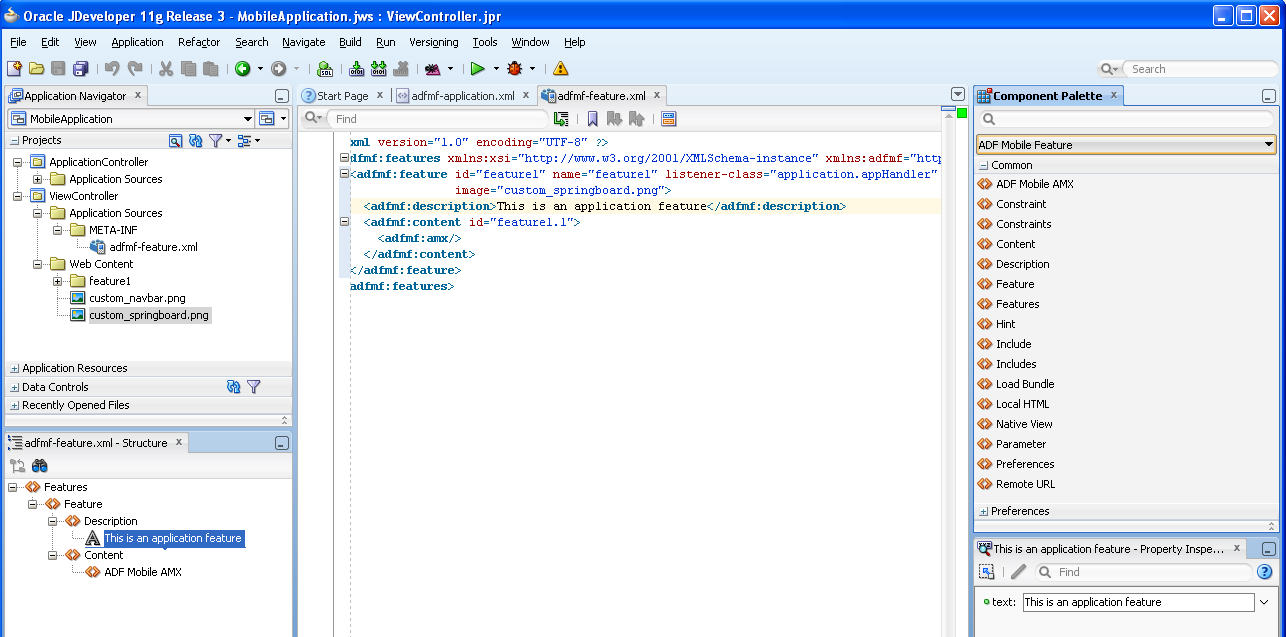
As illustrated in Figure 4-13, the adfmf-feature.xml configuration file is located in the Application Navigator in the Project panel under the view controller and META-INF nodes. You use this file to compose the content for the ADF Mobile application.
Figure 4-13 The Overview Editor for Application Features

Like the overview editor for the adfmf-application.xml file, JDeveloper presents the ADF Mobile components used for building the elements of the adfmf-features.xml configuration file, which are described in Section 5.7, "About the Mobile Feature Application Configuration File." You can use the Overview page or you can drag and drop components from the Component palette into the Structure Window or into the Source editor itself. When you select the adfmf-feature.xml file, JDeveloper populates the Component palette with ADF Mobile Feature components.
Figure 4-14 Using the Source Editor, Structure Window, and Component Palette for Application Features
As described in Chapter 7, "Creating ADF Mobile AMX Pages," the ADF Mobile AMX components enable you to build pages that run identically to those authored in a platform-specific language. These pages may be created by the application assembler, who creates the ADF Mobile application and embeds application features within it, or they can be developed by another developer and then incorporated into the ADF Mobile application either as an application feature or as a resource to an ADF Mobile application.
The project in which you create the ADF Mobile AMX page determines if the page is used to deliver the content for a single application feature or be used as a resource to the entire ADF Mobile application. For example, a page created within the application controller project, as shown in Figure 4-17, would be used as an application-wide resource. An ADF Mobile AMX page created within a view controller project, on the other hand, would be used only to deliver content to an application feature.
An ADF Mobile task flow can likewise be used to deliver the content to an application feature. As shown in Figure 4-15, ADF Mobile provides wizards for adding ADF Mobile AMX pages, task flows, and application features.
To access these wizards, you first select a project within the Application Navigator and then choose File and then New . You select one of the wizards after selecting ADF Mobile within the Client tier.
Figure 4-15 Wizards for Creating Resources for Application Features
You can use the ADF Mobile AMX Page wizard to create AMX pages used as application feature content and separately as a resource to the ADF Mobile application. For more information on application feature content, see Section 5.9.1, "How to Define the Application Content."
To create an ADF Mobile AMX page as content for an application feature:
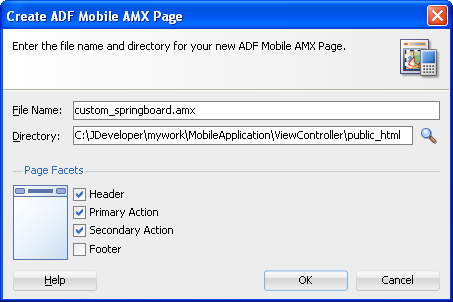
Figure 4-16 Creating an ADF Mobile AMX Page in a View Controller Project
To create an ADF Mobile AMX page as a resource to an ADF Mobile application:
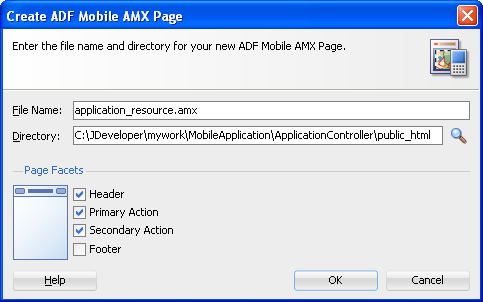
Figure 4-17 Creating an ADF Mobile AMX Page in an Application Controller Project
You can deliver the content for an application feature as an ADF Mobile task flow.
To create an ADF Mobile Task Flow as content for an application feature:
Figure 4-18 Creating an ADF Mobile Task Flow in a View Controller Project
JDeveloper places the ADF Mobile AMX pages and task flows in the Web Content node of the view controller project, as shown by custom_springboard.amx and ViewController-task-flow.xml (the default name for a task flow created within this project) in Figure 4-19. These artifacts are referenced in the adfmf-feature.xml file as described in Section 5.5, "Configuring the Application Features within a Mobile Application." Figure 4-19 also illustrates that other resources, such as customized application splash screen (or launch) images and navigation bar images, are also housed in the Web Content node. For more information, refer to Table 4-3.
Figure 4-19 ADF Mobile AMX Pages and Task Flows within Application Controller and View Controller Projects
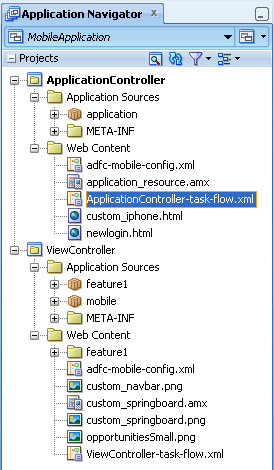
JDeveloper places the ADF Mobile AMX page and task flow as application resources to the ADF Mobile application in the Web Content node of the application controller project. As illustrated in Figure 4-19, the file for the ADF Mobile AMX page is called application_resource.amx and the task flow file is called ApplicationController-task-flow.xml (the default name).